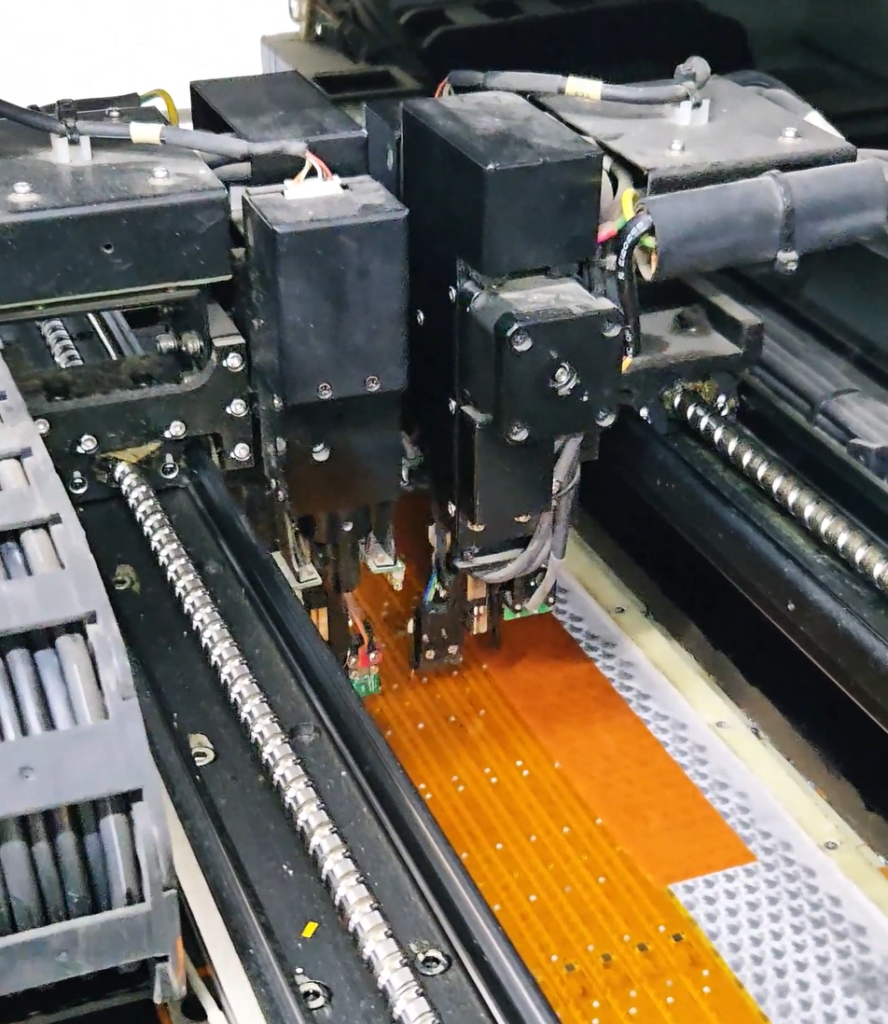
Flying Probe Testing (FPT) is a type of automated electrical testing used to check the functionality and integrity of Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs). Instead of using a bed-of-nails fixture (a traditional testing method), flying probe testers use multiple probes that move across the PCB to make contact with test points, component leads, or vias. These probes are controlled by an automated system, allowing them to move to any location on the PCB and test for short circuits, open circuits, and other potential defects.
How Flying Probe Testing Works?
Moving Probes: In FPT, two or more probes fly across the PCB surface. These probes are typically mounted on precision robotic arms that can quickly move to specific test points based on the PCB’s design.
Contact Points: The probes make contact with copper pads, vias, or other points on the board to measure continuity and resistance, as well as verify connections between layers.
Dynamic Test Creation: Unlike traditional testing, FPT does not require a physical fixture. Instead, it uses the design files (such as Gerber files) to create the testing sequence dynamically, making it more flexible and cost-effective, especially for small production runs and prototypes.
What Advantages of Flying Probe Testing?
1 No Need for Custom Fixtures:
- Traditional bed-of-nails testers require custom-built fixtures, which are expensive and time-consuming to create. Flying probe testing eliminates this need, making it ideal for prototypes and low-volume production where creating a custom fixture is not practical.
2 Cost-Effective:
- Since there is no need for a fixture, setup costs are significantly lower for small batches or prototype runs. This makes FPT a more affordable option for testing boards in the early stages of development or for low-volume production.
3 Quick Turnaround:
- Flying probe systems can be quickly reconfigured to test different PCBs by loading the appropriate test program. This flexibility makes FPT a preferred choice when fast turnarounds are needed, such as in the rapid development and testing phases.
4 High Accuracy:
- The robotic probes are highly accurate, allowing them to test fine-pitch components and small geometries that may be challenging for traditional test fixtures. Additionally, flying probe testers can reach areas that are not accessible by bed-of-nails testers.
5 Comprehensive Testing:
- Flying probe testers can perform a variety of tests, such as continuity testing, short circuit detection, open circuit checks, and component verification (e.g., testing for missing or incorrect components). Some systems can also perform power-up tests to verify the electrical characteristics of the PCB under load.
6 Flexibility for Design Changes:
- FPT is particularly useful during the prototype phase when designs may change frequently. As no fixture is involved, adjustments to the test sequence can be made quickly by modifying the software, allowing easy accommodation for design changes or revisions.
7 Ideal for Complex, Multi-Layer Boards:
- The probes can access both sides of the PCB, and can handle the testing of multi-layer boards with complex routing, blind vias, and buried vias, ensuring that every layer is thoroughly tested.
What Disadvantages of Flying Probe Testing?
1 Slower for Large Volumes:
- FPT is slower than traditional bed-of-nails testers when it comes to high-volume production. For large-scale manufacturing, in-circuit testing (ICT) with a fixture may be more efficient due to its ability to test multiple points simultaneously.
2 Limited Parallel Testing:
- FPT typically tests one point at a time (or a few points, depending on the number of probes), making it less suitable for very high-speed testing compared to methods that can test many points simultaneously.
3 Mechanical Wear:
- Over time, the mechanical probes in FPT can experience wear and tear, requiring calibration or replacement to maintain accuracy, especially for long testing cycles or high usage.
What the Applications of Flying Probe Testing?
- Prototype Testing: FPT is widely used in testing early-stage prototypes to identify potential issues in the PCB layout before moving to large-scale production.
- Low-Volume Production: For small production batches, FPT provides a cost-effective and fast testing solution without the need for costly fixtures.
- Design Validation: FPT allows engineers to validate design changes quickly, providing valuable feedback during the PCB development cycle.
- Multi-Layer and Complex Boards: With its ability to test multi-layer and high-density boards, FPT is well-suited for aerospace, medical, automotive, and telecommunications applications where PCBs are often more complex.
Flying Probe Testing (FPT) is a versatile and cost-effective method for testing prototypes, small production runs, and complex PCBs. It offers flexibility, high accuracy, and quick setup times, making it ideal for applications where design changes are frequent, or large volumes are not yet required. While slower for mass production, FPT remains a valuable tool for early-stage development and low-volume manufacturing, ensuring quality control and product reliability before scaling to high-volume production.

